Pneumatic Comparators
Pneumatic
Comparators
Comparator -
A comparator is a tool,
used to compare the dimensions of a workpiece component with the actual work
standard. Comparators are classified into various kinds, like mechanical,
electronic, electrical, optical, sigma, digital and pneumatic comparators.
Now we will discuss
about Pneumatic Comparator.
Pneumatic Comparator -
Pneumatic Comparators are also
known as Pressure Comparator. And these operated by the gas or air under
pressure that is why they called as Pneumatics.
In Pneumatic Comparator air is used
as the magnification system. Using the Pneumatics, enables two approaches for
measuring the Deflection
1. Measuring
the air pressure
2. Measuring
the Velocity of Airflow
The working response of
the comparator on the Airflow is quite faster than the working response on the
Air Pressure
Parts of Pneumatic
comparator –
- Compressor
- Cylinder (or) water tank
- Air filter
- Pressure regulator
- Dip tube
- Manometer tube
- Control orifice
- Flexible tube
- Gauging head
- Scale
1. Compressor –
In the pneumatic comparator compressor
is produced compressed air and continuously
supplied it and hence compressor is the
main part of pneumatic comparator.
2. Cylinder / Water tank -
The
use of water tank in the Pneumatic comparator is hold the dip tube in it.
3. Air
filter –
The main function of the Air filter in pneumatic comparator is to filter
the dust particles from air which is compressed by compressor.
4. Pressure
regulator –
The main function of Pressure regulator is to regulate the pressure of
compressed air which comes from the air filter.
5. Control
orifice –
Air is supplied at constant pressure through the orifice.
6. Flexible
tube –
Flexible tube is used in the airline to hold the measuring head
7. Gauging
head –
Gauging head is used to measure the irregularities in the workpiece.
There are some types of gauging head such as Type A, Type B, Type C, Type D.
8. Scale
–
Measuring
scale is used to measure the fluid displacement .
Principle of Pneumatic
Comparator –
Pneumatic comparators are based on the
following principle:
When
air escapes from two orifices at constant pressure, the air pressure in the gap
depends on the cross-sectional area of the orifices.
Working principle of
Pneumatic comparator –
In a compressor,
air is compressed at high pressure. This is the same as the water column H.
Excess air escapes as bubbles. A constant amount of matrix air is then passed
through the opening at constant pressure. In position, backpressure is
generated by the water column within the pressure gauge tube. Rotate the plot
along the beam axis to determine the circularity of the plot. If we get no
change in pressure readings, we can say that the plot at location A1 is
perfectly circular. The same procedure is then repeated at different positions
A2, A3, A4. The diameter is also measured at location A1 corresponding to the
cross-section for the two beams, and the diameter is also measured at various
locations along the length of the bore. If the dimension changes, the value of h
also changes. A constant supply pressure is required for high instrument
sensitivity.
Types of Pneumatic comparator:
Basically, the
pneumatic comparators are classified into three types.
·
Flow (or) velocity type pneumatic comparator.
·
Back pressure type pneumatic comparator.
·
Differential pneumatic comparator.
1. Flow or velocity
type pneumatic comparator –
This types of pneumatic comparator operate by
sensing and indicating the momentary rate of airflow. The flow could be sensed
by a glass tube with tapered bore, mounted over a graduated scale, inside the
bore afloat is liſted by the airflow.
The compressed air then
flows through a plastic tube, which is located in the opposite direction with
two identical holes to escape the air. The position of the float depends upon
the amount of air flowing through the gauge head, which in turn depends upon
the clearance between the bore to be measured and the gauging head.
The accuracy of this
comparator is up to 1μm. The magnification of this comparator is
1000,000:1.
2. Back pressure type pneumatic comparator
The back pressure type pneumatic
comparator is constructed using the parts like compressor, filter, pressure
regulator, adjustable restrictor, scale, and measuring head. This pneumatic
comparator consists of two orifices O1 and O2. The orifice O1 is called as control office and the orifice O2 is called as measuring orifice. In the circuit the
compressed air is filtered by an air filter and passes through the pressure
regulator. In the measuring head or gauging head the air escape from the
measuring orifice.
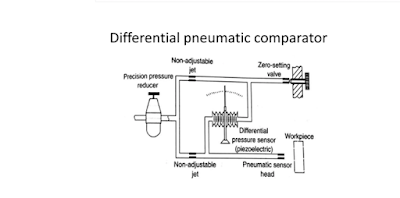
3.
Differential pneumatic comparator
–
This comparator is a type of backpressure pneumatic comparator. The main parts used for its construction are pressure regulator, air filter, compressor, control orifice, reference jet or zero setting valve, pressure indicating device, and measuring head.
Advantages of pneumatic comparator
1.
Inexpensive, easy to use, low cost.
2. No mechanical hysteresis or wear.
3. Magnification up to 10,000x is possible.
4.
The stylus is not in direct contact with the workpiece.
5. Display and measurement he is done in two different locations.
6. Tapers and ellipses are easily recognizable.
7.
The process is self-cleaning due to the continuous flow of air through the nozzle, making it an ideal process to use for on-line checks in workshops.
Disadvantages of pneumatic comparator -
1.They are very sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity.
2. Accuracy may be affected by the surface roughness of the component being tested.
3. A different measuring head is required for each task.
4. Ancillary equipment such as air filters, pressure gauges and regulators are required.
5. Scale non-uniformity is a particular aspect of air measurement, since back pressure variation is linear only over a small range of orifice size variation.
Applications or Uses of Pneumatic comparator 1. Used for inner diameter detection of cylindrical workpieces.
2. The inner diameter and outer diameter of the workpiece can be recognized.
3. The straightness and flatness of the workpiece can be recognized.
4. You can easily analyze the taper and ellipticity of the workpiece.
5. Also used to check the roundness and squareness of workpieces.
6. Depending on the type of measuring head and number of orifices, pneumatic comparators have different application.




Comments
Post a Comment